Cannabidiol (CBD)
CBD is a naturally derived compound extracted from industrial hemp
Key words:
Haigu Biology
Cannabidiol
Biotechnology
Industrial hemp
Classification:
Product Description
Product Description (Specifications, Models, Structural Principles, Performance Indicators, Functions, Uses, Components, Processing Methods, Analysis Methods, etc.):
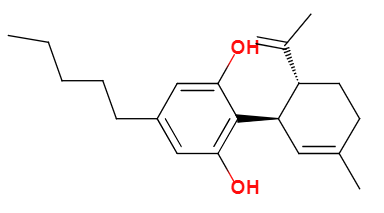
Specifications: 1 kg/bottle, 5 kg/bottle, 10 kg/bottle; Molecular Formula: C21H30O2; Molecular Weight: 314.46; Melting Point: 66–67°C; almost insoluble in water or 10% sodium hydroxide solution, but soluble in ethanol, methanol, ether, benzene, chloroform, and petroleum ether.
CBD is a naturally derived compound extracted from industrial hemp. In addition to mitigating the adverse effects of polyphenols like THC on the human nervous system, it exhibits various physiological benefits, such as inhibiting breast cancer metastasis, treating epilepsy, addressing rheumatoid arthritis, and promoting sleep. In 2003, a US-based company applied for a patent recognizing CBD as a neuroprotectant and antioxidant. Recently, low concentrations of CBD have been applied in health supplements, food, and skincare products, and thus have been gradually recognized by consumers. The following describes some of the current applications of CBD.
CBD is a naturally derived compound extracted from the flowers and leaves of industrial hemp. To get it, we adopt a process involving counter-current extraction, low-temperature dewaxing, heat decarboxylation, molecular distillation for enrichment and impurity removal, as well as preparative chromatography for purification and isolation. Tested through high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), it has been proved that the CBD content ranges from 60% to 80%, and that the THC impurity limit is less than 0.3%.
Chinese name: Cannabidiol (CBD)
Chinese alias: polyphenol resin (chemistry)
CAS No:13956-29-1
English name: Cannabidiol
Molecular formula: C21H30O2
Molecular weight: 314.46
Structural formula:
Related Products
Inquiry








